The Decision Support Systems Laboratory of the National Technical University of Athens (DSSLab-NTUA) is one of the key partners of the Enershare Horizon Europe project leading several research activities and the implementation of multiple critical parts of the technical solution under development, in parallel with the pilot coordination within the project. The overall vision of Enershare is to develop and demonstrate a European common energy data space that will develop an “intra-energy” and “cross-sectoral” interoperable and reliable energy data ecosystem. Private consumers, business (energy and non-energy) stakeholders and regulated operators will be able to access, share and reuse, based on voluntary agreements: (a) Large sources of currently fragmented and dispersed data. (b) Data-driven cross-price, chain services (energy and non-energy) and Digital Twins for various purposes. In the Enershare project, while pursuing collaborations and interoperability between sister projects that make up the Common European Energy Data Space (SYNERGIES, IntNet, OMEGA-X, Enershare, DATA CELLAR, SYNERGIES and EDDIE) we tend towards creating new partnerships and ultimately promoting the vision for a fully interoperable energy data space.
In this direction, DSSLab-NTUA authored a study entitled: “Enhancing Green Finance through AI Analytics and Cross-Domain Data Sharing”. The study deep dives into the field of green finance, which has gained increasing international interest in recent years and can contribute to green growth towards tackling climate change as well as the emerging technology of data sharing and artificial intelligence (AI). More specifically, the study explores ways to leverage existing and innovative methods and technologies related to financial “green” products, such as green bonds, in parallel with research programs aimed at promoting green investments. In this context, we are exploring whether AI and data sharing between organisations and sectors can be effectively exploited to address the lack of information on green investments. Therefore, we are demonstrating that by finding and exploiting data through various techniques and sharing data between stakeholders, it is possible to optimize and solve issues that will promote sustainable development, thus opening an innovative and necessary path to the green transition.
As proof of concept, two ongoing case studies in the fields of energy and green deals, supported by the emerging technology of European Data Spaces are also analyzed. The connectivity of Data Spaces in both cases refers to the connection of the digital data space between the different services and data sources within the project environments. This connection enables secure and efficient data exchange between services and the Data Space ecosystem.
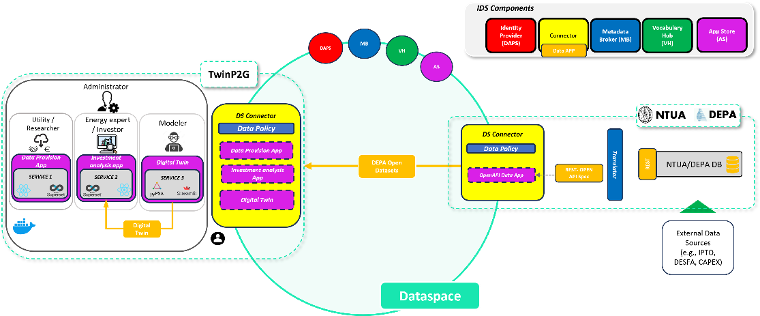
Regarding the first case study, it illustrates DEPA’s (a natural gas trader in Greece) digital twin services in the ENERSHARE Data Space. DEPA’s digital twin services are aimed at a combined optimisation platform (i.e., TwinP2G) coupling the electricity transmission system with natural gas demands, leveraging a Digital Twin (DT) architecture that will enable multi-resolution simulations involving P2G technologies and (regenerative) hydrogen fuel cells. TwinP2G will enable data- and simulation-driven P2G and RHFC optimal planning leveraging RES surplus for green hydrogen production via electrolysis and/or methanation. The figure showcases the architecture of the different services and components linked together for the provision of digital services in the energy sector. It also presents the interconnection of the digital twin with the EnerShare Data Space through IDS links, which ensure the secure exchange of data and the interaction between services and data sources within the data space.
With respect to the second case study, it refers to a LEIF, a Latvian Environmental Investment Fund. The aim of LEIF is to create a solid framework through cross-sectoral integration of data on financial performance of energy efficiency projects. The scope is to strengthen debt and equity financing of energy efficiency investments, providing investors and project developers the opportunity to easily evaluate key performance indicators of future projects. Besides traditional AI-based green financing analytics services, in the context of this pilot the evaluation of energy data sharing to other sectors and the exploitation of how this pilot concept should evolve to become a more generic data sharing solution are investigated. The figure below demonstrates AI4EF and its interconnection with the Enershare Data Space. AI4EF is provided as a publicly available tool for the owners of private houses that intend to determine whether to invest in their building or in the installation of renewable energy resource technologies. The stakeholders include owners of private houses, ministries and institutions that grant public support.

